In the dynamic world of cybersecurity, where new vulnerabilities emerge faster than ever, organizations must stay vigilant to safeguard their critical infrastructure. As attackers target widely deployed security solutions like Palo Alto Networks and Fortinet, the stakes couldn’t be higher. These technologies, while integral to defending against threats, also represent high-value targets for adversaries seeking to exploit weaknesses in firewalls, migration tools, and configuration settings.
In 2024, key vulnerabilities in both Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS and Fortinet’s FortiGate firewalls underscore the importance of proactive defense measures. From authentication bypasses and SQL injections to denial-of-service vulnerabilities, these issues highlight how even robust systems can become attack vectors when exploited. Below, we explore some of the most impactful vulnerabilities discovered in these platforms this year and their implications for organizations relying on these critical technologies.
The 2024 Spotlight on Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS: Critical Vulnerabilities and Lessons Learned
Palo Alto Networks’ PAN-OS, the backbone of many firewalls and security appliances, stands as a cornerstone in modern cybersecurity infrastructure. Its extensive adoption has made it a top target for attackers aiming to bypass defenses and exploit vulnerabilities for malicious gains. Recent discoveries in 2024 underscore the importance of vigilance, timely updates, and robust security configurations.
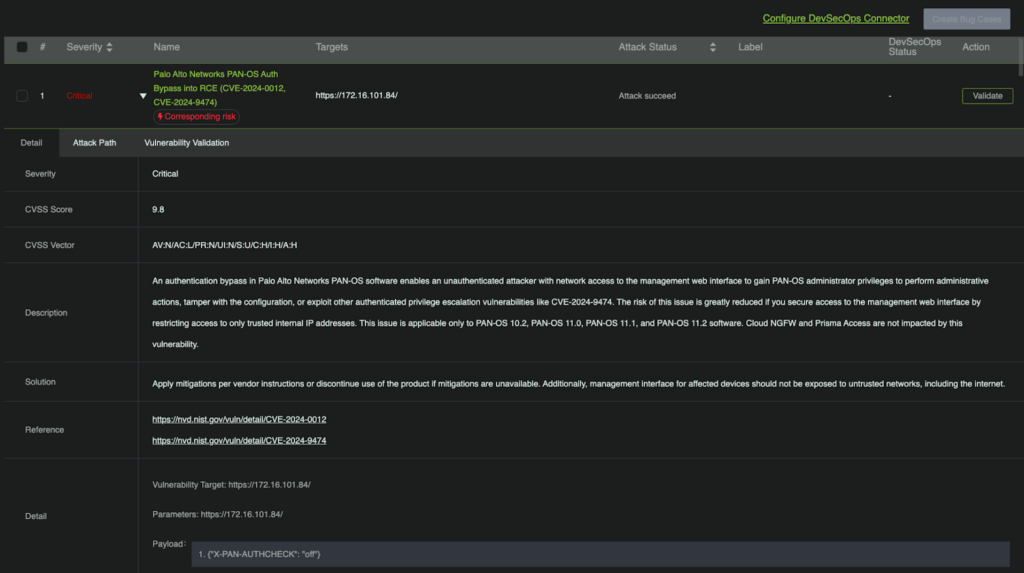
One particularly alarming flaw in PAN-OS involves bypassing authentication entirely using a deceptively simple HTTP header “(X-PAN-AUTHCHECK: off)”. This trivial exploit opens the door to administrative privileges, enabling attackers to alter configurations or execute unauthorized code. Compromising a firewall at this level hands over the keys to the kingdom, exposing the entire network. Implementing strict IP whitelisting on the administrative interface is a frontline defense, reducing the risk of such breaches.
Vulnerabilities are not limited to PAN-OS itself; ancillary tools such as the Expedition firewall migration tool can inadvertently leave sensitive endpoints exposed post-setup. Attackers exploiting these endpoints could gain administrative control, harvest credentials, and manipulate critical configurations. Further, the possibility of SQL injection in Expedition allows attackers to modify databases, extract sensitive data, or execute arbitrary commands on the underlying server. These threats highlight how even helpful utility tools can become liabilities if not deployed and maintained securely.
The vulnerabilities uncovered in PAN-OS during 2024, including denial-of-service attacks via DNS queries and root-level access through GlobalProtect flaws, are just part of the picture. Numerous other critical flaws, many of which were deemed significant enough by the U.S. government to be added to the CISA KEV list, highlight weaknesses across various areas of the system. These exploits demonstrate how easily attackers can disable firewalls, compromise systems, and turn trusted devices into threats. To address these risks, organizations must prioritize timely updates, enforce strict access controls, and secure administrative interfaces against unauthorized access. These challenges serve as a reminder that proactive, comprehensive security measures are essential, as even minor oversights can cascade into severe breaches, operational disruptions, and data loss.
Fortinet Under Fire: Widespread Usage and High-Profile CVEs
Palo Alto Networks’ challenges in 2024 are substantial, but they are not alone. Fortinet—specifically its FortiGate line of firewalls—faces similar threats due to its widespread deployment, making it an attractive target for cybercriminals. The Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) list highlights 15 CVEs related to Fortinet, with 11 of them enabling unauthorized remote attackers to directly compromise a system.
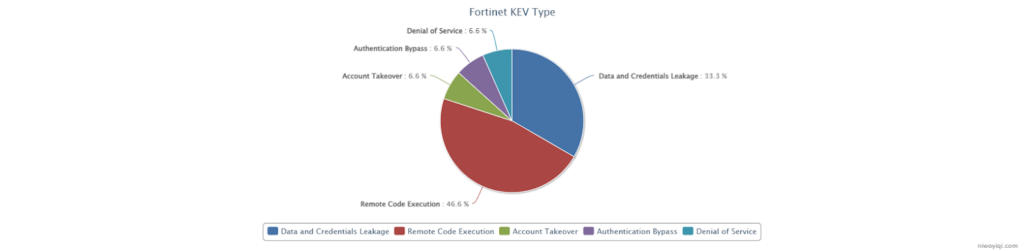
In 2024, three Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerabilities were added to the KEV list. These vulnerabilities are particularly dangerous because they allow attackers to execute malicious code, potentially leading to complete device control, network breaches, data theft, and service disruptions. RCE vulnerabilities in Fortinet devices are especially critical as these devices often serve as the network’s first line of defense, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
In addition to RCE vulnerabilities, Fortinet faces significant risks from credential and data leakage vulnerabilities. These exposures can reveal sensitive information like login credentials, network configurations, and private data, allowing attackers to bypass security measures, escalate privileges, and compromise the network. Leaked credentials can facilitate device takeovers, unauthorized data access, and lateral attacks within the network.
Other notable vulnerabilities include Denial of Service (DoS), Authentication Bypass, and Account Takeover. While the number of these CVEs may not be large, they are equally dangerous, often leading to the circumvention of security protections and exposure of internal systems.
In one word, Fortinet faces critical challenges due to RCE, credential leakage, and other vulnerabilities that can lead to system compromise and network breaches. These vulnerabilities, especially in widely deployed FortiGate firewalls, make Fortinet a prime target for cyberattacks.
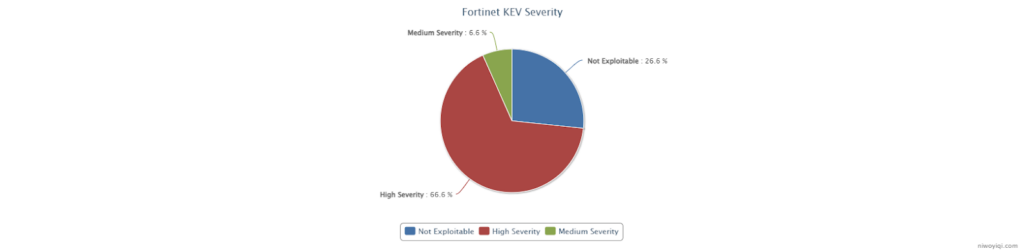
Known Exploited Fortinet CVEs
15 CVEs on the KEV List
11 can be exploited without any privileges or local network access—giving attackers partial or full control of the system and allowing them to potentially turn Fortinet products against the very networks they are meant to protect.
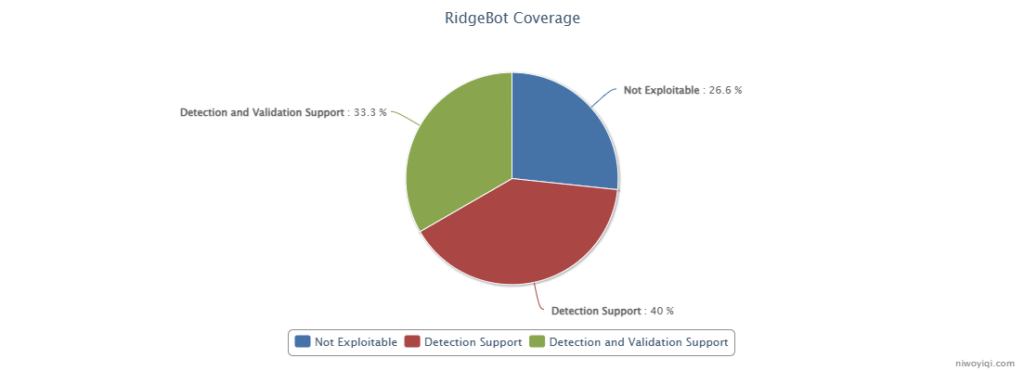
RidgeBot Coverage for Fortinet
Detection Plugins for All 11 Unauthenticated CVEs: RidgeBot can detect and report these vulnerabilities, ensuring that you address them before attackers do.
Validation Plugins for 5 CVEs: By demonstrating the real impact of successful exploitation, these plugins help prioritize remediation efforts.
Beyond KEV-Listed Vulnerabilities
Beyond the KEV-listed CVEs, RidgeBot also supports four additional Fortinet vulnerabilities—three high severity and one medium—that, while not yet reported to be exploited in the wild, have publicly available Proof of Concepts (POCs). Attackers could potentially leverage these weaknesses, making RidgeBot’s coverage crucial for a truly comprehensive defense.
RidgeBot: Real-Time Protection for Both Palo Alto Networks and Fortinet
Whether you rely on Palo Alto Networks or Fortinet solutions, or both, RidgeBot continuously protects your systems by delivering real-time plugin updates to address emerging threats. By simulating real-world attacks, RidgeBot detects vulnerabilities and provides actionable remediation guidance. From authentication bypasses to SQL injections and critical misconfigurations, RidgeBot is designed to scale with infrastructures of all sizes, reducing your attack surface and ensuring broad coverage with its evolving plugin library.
With Ridge Securit’s RidgeBot AI-powered automated testing, customers can quickly find all potential risks in their entire network. Once vulnerabilities are discovered, RidgeBot provides detailed reports including the type, severity, description, and other pertinent details. With this information, it will be easy to understand what the vulnerabilities are, their impact, and how to patch them.
In the Information Age, cyber threats are everywhere. Ridge Security continuously monitors emerging vulnerabilities to protect our customers. With our ever-growing threat intelligence database, RidgeBot provides unparalleled defense against evolving cyber threats, giving you peace of mind and robust protection in an ever-evolving threat landscape. Please contact us to request a free demo.