What is OWASP Top 10?
Security breaches and attacks have become so prevalent that only the very largest ones now make the headlines. But attacks against organizations of all sizes have never been so rife or so sophisticated, making it all the more critical that you do everything you can to protect your organization’s digital assets.
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a non-profit organization that works towards raising awareness, improving, and managing web application security risks. Virtually all businesses and other public/private organizations in today’s digital economy maintain web applications and servers to advertise, buy, sell, inform, and serve their customers or members in countless ways. By definition, a web application is public-facing: this makes it especially vulnerable to exploits from anywhere at any time. To protect your organization against security attacks and breaches, it is imperative to manage closely the vulnerabilities in web application software interactions.
OWASP evaluates the most prevalent and critical web application vulnerabilities to produce a Top 10 list that is updated every 3-4 years. The most recent report was published in 2021. The OWASP Top 10 project uses broad industry consensus to determine the 10 most critical web application security risk categories. Well- known industry CWEs (Common Weakness Enumeration) are mapped into the Top 10 categories. The CWEs in turn draw on a larger database of CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) maintained in the National Vulnerability Database (NVD) under the direction of the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework.
Understanding the OWASP Top 10 Categories
The 2021 Top 10 OWASP vulnerabilities are:
A01: 2021-Broken Access Control: Improper enforcement of restrictions on what authenticated users are allowed to do, enables attackers to exploit access to unauthorized functionality and/or data.
A02: 2021- Cryptographic Failures Many web applications and APIs do not properly protect sensitive data, such as financial, healthcare, and personally identifiable information (PII), allowing attackers to steal or modify such data to conduct fraud, identity theft, or other crimes.
A03:2021-Injection Injection flaws, such as SQL, NoSQL, OS, and LDAP injection, occur when untrusted data is sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query.
A04:2021-Insecure Design is a new category for 2021, with a focus on risks related to design flaws.
A05:2021-Security Misconfiguration Security misconfiguration is the most commonly seen issue, including insecure default configurations, incomplete or ad hoc configurations, open cloud storage, misconfigured HTTP headers, and verbose error messages containing sensitive information. A4:2017-XML External Entities (XXE) is now part of this risk category.
A06:2021-Vulnerable and Outdated Components Exploiting a vulnerable component— such as libraries, frameworks, and other software modules that run with the same privileges as the application—can lead to serious data loss or server takeover.
A07:2021- Identification and Authentication Failures Authentication and session management functions implemented incorrectly, allow attackers to compromise passwords, keys, or session tokens to exploit user identities.
A08:2021- Software and Data Integrity Failures is a new category making assumptions related to software updates, critical data, and CI/CD pipelines without verifying integrity. A8:2017-Insecure Deserialization is now a part of this larger category.
A09:2021-Security Logging and Monitoring Failures Insufficient logging and monitoring, coupled with missing or ineffective integration with incident response, allows attackers to further attack systems, maintain persistence, pivot to more systems, and tamper with, extract, or destroy data.
A10:2021-Server-Side Request Forgery allows an attacker to induce the server-side application to make HTTP requests to an arbitrary domain of the attacker’s choosing.
Ridge Security’s CWE to OWASP Top 10 Mapping
The OWASP Top 10 categories provide an easy, clear at-a-glance summary of the ten most critical web application security risks. To protect your organization’s web applications and servers, you must understand which specific vulnerabilities (CWEs) are included in each of the OWASP Top 10 categories.
While there is broad industry agreement on mapping CWEs to OWASP categories, there are differences in the specific implementations by different security mitigation vendors’ products. These details matter to the breadth of coverage and protection you get from using a specific vendor’s product to pentest your web applications.
RidgeBot covers a comprehensive list of CWEs in each OWASP Top 10 category, providing you with the highest confidence that RidgeBot’s pentest and exploitation capabilities result in thorough protection of your organization’s web application and servers.
A1:2021-Broken Access Control
- CWE-22—Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (‘Path Traversal’)
- CWE-23—Relative Path Traversal
- CWE-35—Path Traversal: ‘…/…//’
- CWE-59—Improper Link Resolution Before File Access (‘Link Following’)
- CWE-200—Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor
- CWE-201—Exposure of Sensitive Information Through Sent Data
- CWE-219—Storage of File with Sensitive Data Under Web Root
- CWE-264—Permissions, Privileges, and Access Controls (should no longer be used)
- CWE-275—Permission Issues
- CWE-276—Incorrect Default Permissions
- CWE-284—Improper Access Control
- CWE-285—Improper Authorization
- CWE-352—Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
- CWE-359—Exposure of Private Personal Information to an Unauthorized Actor
- CWE-377—Insecure Temporary File
- CWE-402—Transmission of Private Resources into a New Sphere (‘Resource Leak’)
- CWE-425—Direct Request (‘Forced Browsing’)
- CWE-441—Unintended Proxy or Intermediary (‘Confused Deputy’)
- CWE-497—Exposure of Sensitive System Information to an Unauthorized Control Sphere
- CWE-538—Insertion of Sensitive Information into Externally-Accessible File or Directory
- CWE-540—Inclusion of Sensitive Information in Source Code
- CWE-548—Exposure of Information Through Directory Listing
- CWE-552—Files or Directories Accessible to External Parties
- CWE-566—Authorization Bypass Through User-Controlled SQL Primary Key
- CWE-601—URL Redirection to Untrusted Site (‘Open Redirect’)
- CWE-639—Authorization Bypass Through User-Controlled Key
- CWE-651—Exposure of WSDL File Containing Sensitive Information
- CWE-668—Exposure of Resource to Wrong Sphere
- CWE-706—Use of Incorrectly-Resolved Name or Reference
- CWE-862—Missing Authorization
- CWE-863—Incorrect Authorization
- CWE-913—Improper Control of Dynamically-Managed Code Resources
- CWE-922—Insecure Storage of Sensitive Information
- CWE-1275—Sensitive Cookie with Improper SameSite Attribute
A2:2021-Cryptographic Failures
- CWE-261—Weak Encoding for Password
- CWE-296—Improper Following of a Certificate’s Chain of Trust
- CWE-310—Cryptographic Issues
- CWE-319—Cleartext Transmission of Sensitive Information
- CWE-321—Use of Hard-coded Cryptographic Key
- CWE-322—Key Exchange without Entity Authentication
- CWE-323—Reusing a Nonce, Key Pair in Encryption
- CWE-324—Use of a Key Past its Expiration Date
- CWE-325—Missing Required Cryptographic Step
- CWE-326—Inadequate Encryption Strength
- CWE-327—Use of a Broken or Risky Cryptographic Algorithm
- CWE-328—Reversible One-Way Hash
- CWE-329—Not Using a Random IV with CBC Mode
- CWE-330—Use of Insufficiently Random Values
- CWE-331—Insufficient Entropy
- CWE-335—Incorrect Usage of Seeds in Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG)
- CWE-336—Same Seed in Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG)
- CWE-337—Predictable Seed in Pseudo- Random Number Generator (PRNG)
- CWE-338—Use of Cryptographically Weak Pseudo-Random Number Generator (PRNG)
- CWE-340—Generation of Predictable Numbers or Identifiers
- CWE-347—Improper Verification of Cryptographic Signature
- CWE-523—Unprotected Transport of Credentials
- CWE-720—OWASP Top Ten 2007 Category A9 – Insecure Communications
- CWE-757—Selection of Less-Secure Algorithm During Negotiation (‘Algorithm Downgrade’)
- CWE-759—Use of a One-Way Hash without a Salt
- CWE-760—Use of a One-Way Hash with a Predictable Salt
- CWE-780—Use of RSA Algorithm without OAEP
- CWE-818—Insufficient Transport Layer Protection
- CWE-916—Use of Password Hash With Insufficient Computational Effort
A3:2021-Injection
- CWE-20—Improper Input Validation
- CWE-74—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements in Output Used by a Downstream Component (‘Injection’)
- CWE-75—Failure to Sanitize Special Elements into a Different Plane (Special Element Injection)
- CWE-77—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in a Command (‘Command Injection’)
- CWE-78—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an OS Command (‘OS Command Injection’)
- CWE-79—Improper Neutralization of Input During Web Page Generation (‘Cross-site Scripting’)
- CWE-80—Improper Neutralization of Script-Related HTML Tags in a Web Page (Basic XSS)
- CWE-83—Improper Neutralization of Script in Attributes in a Web Page
- CWE-87—Improper Neutralization of Alternate XSS Syntax
- CWE-88—Improper Neutralization of Argument Delimiters in a Command (‘Argument Injection’)
- CWE-89—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an SQL Command (‘SQL Injection’)
- CWE-90—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an LDAP Query (‘LDAP Injection’)
- CWE-9—XML Injection (aka Blind XPath Injection)
- CWE-93—Improper Neutralization of CRLF Sequences (‘CRLF Injection’)
- CWE-94—Improper Control of Generation of Code (‘Code Injection’)
- CWE-95—Improper Neutralization of Directives in Dynamically Evaluated Code (‘Eval Injection’)
- CWE-96—Improper Neutralization of Directives in Statically Saved Code (‘Static Code Injection’)
- CWE-97—Improper Neutralization of Server-Side Includes (SSI) Within a Web Page
- CWE-98—Improper Control of Filename for Include/Require Statement in PHP Program (‘PHP Remote File Inclusion’)
- CWE-99—Improper Control of Resource Identifiers (‘Resource Injection’)
- CWE-100—Deprecated: Was catch-all for input validation issues
- CWE-113—Improper Neutralization of CRLF Sequences in HTTP Headers (‘HTTP Response Splitting’)
- CWE-116—Improper Encoding or Escaping of Output
- CWE-138—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements
- CWE-184—Incomplete List of Disallowed Inputs
- CWE-470—Use of Externally-Controlled Input to Select Classes or Code (‘Unsafe Reflection’)
- CWE-471—Modification of Assumed- Immutable Data (MAID)
- CWE-564—SQL Injection: Hibernate
- CWE-610—Externally Controlled Reference to a Resource in Another Sphere
- CWE-643—Improper Neutralization of Data within XPath Expressions (‘XPath Injection’)
- CWE-644—Improper Neutralization of HTTP Headers for Scripting Syntax
- CWE-652—Improper Neutralization of Data within XQuery Expressions (‘XQuery Injection’)
- CWE-917—Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an Expression Language Statement (‘Expression Language Injection’)
A4:2021-Insecure Design
- CWE-73—External Control of File Name or Path
- CWE-183—Permissive List of Allowed Inputs
- CWE-209—Generation of Error Message Containing Sensitive Information
- CWE-213—Exposure of Sensitive Information Due to Incompatible Policies
- CWE-235—Improper Handling of Extra Parameters
- CWE-256—Unprotected Storage of Credentials
- CWE-257—Storing Passwords in a Recoverable Format
- CWE-266—Incorrect Privilege Assignment
- CWE-269—Improper Privilege Management
- CWE-280—Improper Handling of Insufficient Permissions or Privileges
- CWE-31—Missing Encryption of Sensitive Data
- CWE-312—Cleartext Storage of Sensitive Information
- CWE-313—Cleartext Storage in a File or on Disk
- CWE-316—Cleartext Storage of Sensitive Information in Memory
- CWE-419—Unprotected Primary Channel
- CWE-430—Deployment of Wrong Handler
- CWE-434—Unrestricted Upload of File with Dangerous Type
- CWE-444 —Inconsistent Interpretation of HTTP Requests (‘HTTP Request Smuggling’)
- CWE-451—User Interface (UI) Misrepresentation of Critical Information
- CWE-472—External Control of Assumed- Immutable Web Parameter
- CWE-501—Trust Boundary Violation
- CWE-522—Insufficiently Protected Credentials
- CWE-525—Use of Web Browser Cache Containing Sensitive Information
- CWE-539—Use of Persistent Cookies Containing Sensitive Information
- CWE-579—J2EE Bad Practices: Non- serializable Object Stored in Session
- CWE-598—Use of GET Request Method With Sensitive Query Strings
- CWE-602—Client-Side Enforcement of Server-Side Security
- CWE-642—External Control of Critical State Data
- CWE-646—Reliance on File Name or Extension of Externally-Supplied File
- CWE-650—Trusting HTTP Permission Methods on the Server Side
- CWE-653—Insufficient Compartmentalization
- CWE-656—Reliance on Security Through Obscurity
- CWE-657—Violation of Secure Design Principles
- CWE-799—Improper Control of Interaction Frequency
- CWE-807—Reliance on Untrusted Inputs in a Security Decision
- CWE-840—Business Logic Errors
- CWE-841—Improper Enforcement of Behavioral Workflow
- CWE-927—Use of Implicit Intent for Sensitive Communication
- CWE-1021—Improper Restriction of Rendered UI Layers or Frames
- CWE-1173—Improper Use of Validation Framework
A5:2021-Security Misconfiguration
- CWE-2—Configuration
- CWE-11—ASP.NET Misconfiguration: Creating Debug Binary
- CWE-13—ASP.NET Misconfiguration: Password in Configuration File
- CWE-15—External Control of System or Configuration Setting
- CWE-16—Configuration
- CWE-260—Password in Configuration File
- CWE-315—Cleartext Storage of Sensitive Information in a Cookie
- CWE-520—NET Misconfiguration: Use of Impersonation
- CWE-526—Exposure of Sensitive Information Through Environmental Variables
- CWE-537—Java Runtime Error Message Containing Sensitive Information
- CWE-541—Inclusion of Sensitive Information in an Include File
- CWE-547—Use of Hard-coded, Security-relevant Constants
- CWE-611—Improper Restriction of XML External Entity Reference
- CWE-614—Sensitive Cookie in HTTPS Session Without ‘Secure’ Attribute
- CWE-756—Missing Custom Error Page
- CWE-776—Improper Restriction of Recursive Entity References in DTDs (‘XML Entity Expansion’)
- CWE-942—Overly Permissive Cross-domain Whitelist
- CWE-1004—Sensitive Cookie Without ‘HttpOnly’ Flag
- CWE-1032—OWASP Top Ten 2017 Category A6 – Security Misconfiguration
- CWE-1174—ASP.NET Misconfiguration: Improper Model Validation
A6:2021-Vulnerable and Outdated Components
- CWE-937—OWASP Top 10 2013: Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- CWE-1035—2017 Top 10 A9: Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
- CWE-1104—Use of Unmaintained Third Party Components
A7:2021-Identification and Authentication Failures
- CWE-255—Credentials Management Errors
- CWE-259—Use of Hard-coded Password
- CWE-287—Improper Authentication
- CWE-288—Authentication Bypass Using an Alternate Path or Channel
- CWE-290—Authentication Bypass by Spoofing
- CWE-294—Authentication Bypass by Capture-replay
- CWE-295—Improper Certificate Validation
- CWE-297—Improper Validation of Certificate with Host Mismatch
- CWE-300—Channel Accessible by Non- Endpoint
- CWE-302—Authentication Bypass by Assumed-Immutable Data
- CWE-304—Missing Critical Step in Authentication
- CWE-306—Missing Authentication for Critical Function
- CWE-307—Improper Restriction of Excessive Authentication Attempts
- CWE-346—Origin Validation Error
- CWE-384—Session Fixation
- CWE-521—Weak Password Requirements
- CWE-613—Insufficient Session Expiration
- CWE-620—Unverified Password Change
- CWE-640—Weak Password Recovery Mechanism for Forgotten Password
- CWE-798—Use of Hard-coded Credentials
- CWE-940—Improper Verification of Source of a Communication Channel
- CWE-1216—Lockout Mechanism Errors
A8:2021-Software and Data Integrity Failures
- CWE-345—Insufficient Verification of Data Authenticity
- CWE-353—Missing Support for Integrity Check
- CWE-426—Untrusted Search Path
- CWE-494—Download of Code Without Integrity Check
- CWE-502—Deserialization of Untrusted Data
- CWE-565—Reliance on Cookies without Validation and Integrity Checking
- CWE-784—Reliance on Cookies without Validation and Integrity Checking in a Security Decision
- CWE-829—Inclusion of Functionality from Untrusted Control Sphere
- CWE-830—Inclusion of Web Functionality from an Untrusted Source
- CWE-915—Improperly Controlled Modification of Dynamically-Determined Object Attributes
A9:2021-Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
- CWE-117—Improper Output Neutralization for Logs
- CWE-223—Omission of Security-relevant Information
- CWE-532—Insertion of Sensitive Information into Log File
- CWE-778—Insufficient Logging
A10:2021-Server-Side Request Forgery
- CWE-918—Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
How a RidgeBot OWASP Top 10 Report Helps with Security Audits
Because the CWE to OWASP TOP 10 mappings vary among vendor implementations, the statement that your organization is “OWASP Top 10” compliant remains ambiguous. During an audit you may have to provide detailed evidence of protection for each of the specific CWEs that you, or the auditor, believe makes you OWASP compliant.
RidgeBot’s comprehensive built-in OWASP report streamlines providing evidence to management or auditors that all your web applications are OWASP Top 10 compliant.
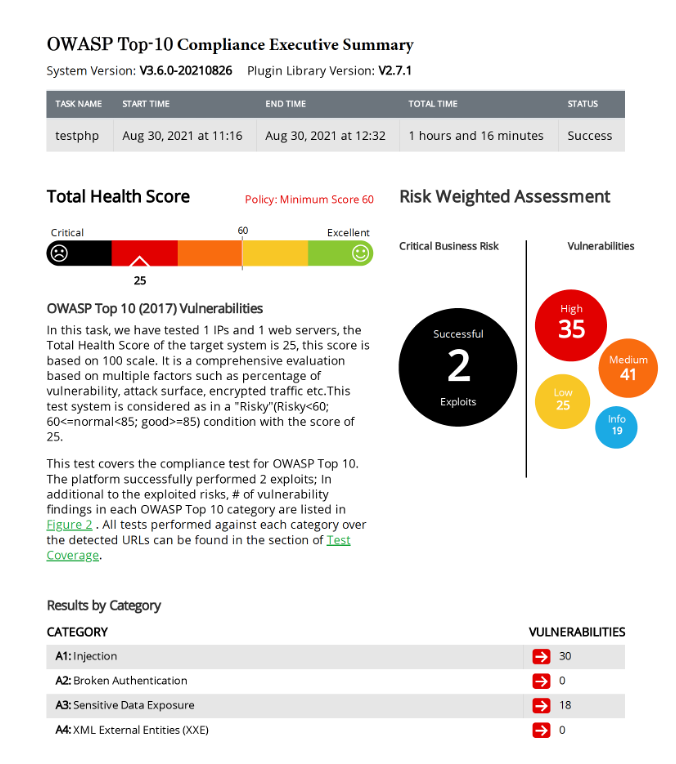
The header of the RidgeBot OWASP Top 10 report gives an executive summary of all the vulnerabilities found—classified into appropriate levels of severity—as well as those that were successfully exploited (red arrow). Further down (green arrow), the report provides detailed compliance information for each of the OWASP Top 10 categories and for the exact CWEs tested in each category.
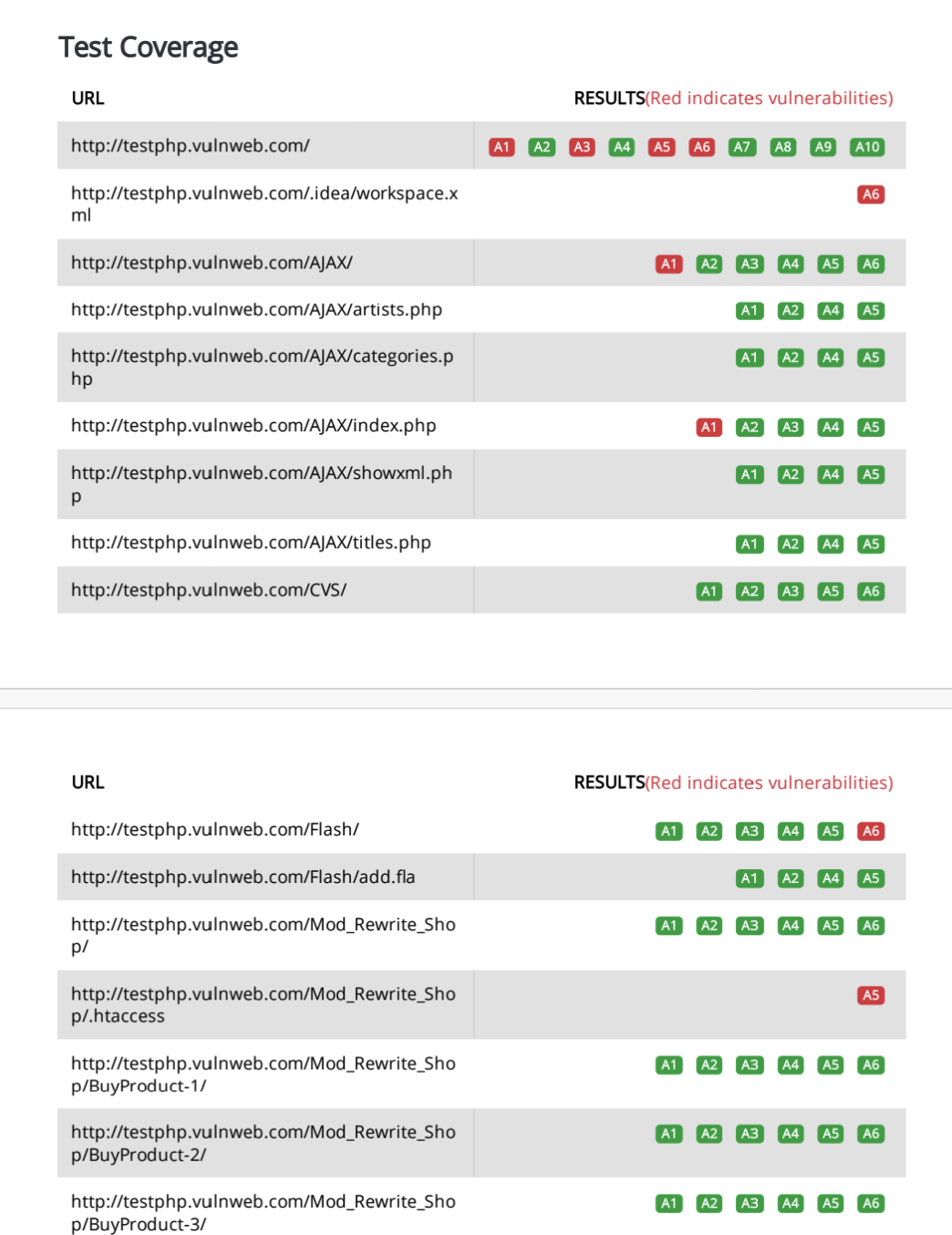
For each of the servers you subjected to RidegBot web penetration testing and exploitation, the body of the report indicates the compliance status of each of the OWASP Top 10 categories. This information gives you an instant roadmap to patch, upgrade or replace your applications to become compliant. It also gives you ready evidence to present to an auditor that your applications and servers are compliant.
The Benefits of Using RidgeBot to Maintain Protection Against OWASP Top 10
The OWASP community provides helpful information and tools to address web application security risks. While the Top 10 list is an extremely helpful and broad industry benchmark, it does not ease the burden of implementing a strategy to know how your web applications measure up, or how to fix lingering vulnerabilities. The Top 10 list also does not provide specifics of which exact CWEs your applications are protected against.
A RidgeBot pen-testing and exploitation run targets a comprehensive and industry- superior set of CWE vulnerabilities in each Top 10 category. The built-in report provides exact details of every Top 10 category and CWE tested and/or exploited. With a periodic—the frequency of your choosing—RidgeBot test-exploit against your web servers and applications you can always rest assured that your organization’s digital assets are as secure as possible from reigning web-based attacks. You can provide on-demand information and evidence to management or auditors about the state of compliance of your organization’s web-based activities. The report also includes detailed steps for resolving any vulnerabilities found—and the relative priority of each—that can guide staff on the specific actions to take to become or maintain 100% compliance.
Please complete the form to download the OWASP sample report.
Please complete the form to download the sample report.
![OWASP-Top-10-08032023[13724]](https://ridgesecurity.ai/wp-content/uploads/OWASP-Top-10-0803202313724.png)
